
- RedDot CMS Blog
- 03.03.2017
- EN
rdb: How to incorporate SEO best practises within RedDot CMS projects
The two main goals every website should try to achieve is to attract and convert visitors, whether it be the form of leads, sales, or an increase in readership. From a development point of view, implementing SEO best practises within your CMS projects will help your site to gain exposure by enabling search engine web crawlers to effectively explore and index site pages.
Unfortunately there isn’t any fancy plugins or in-built functionality within RedDot that will automatically optimise your site. But don’t worry, making your site ‘SEO Friendly’ is relatively straight forward and easy to do!
Below are some helpful hints that will help you to optimise your RedDot CMS projects:
Alternate keyword rich page titles
The title tag is the single most important piece of information that search engines use when deciphering your web pages, therefore it is important that authors can insert target keyword and phrases within this title.
In most projects, the default page ‘headline’ placeholder is used to automatically populate the title, page name displayed in the body content (h1) and the link name where the page appears within the site navigation. For this reason displaying long, ‘keyword rich’ titles across your entire site is not a good look!
Don’t worry about making this field mandatory; just use a render tag or a pre-executing script block to default to the page headline value if no alternate page title is entered. I would suggest limiting this value to around 120 characters.
Meta Tags
As a minmum, ensure that you provide authors with the ability to enter in description and keyword meta values for the page.
The meta description value shows up in many search engine results as a summary for your page. Google, in particular, will display full snippets of the description value when a keyword phrase or sequence matches the search query. It is important to provide a creative, well written, compelling summary for your page in order to drive ‘click-through’ traffic from search engines. Limit the description value to around 160 characters and make it a mandatory placeholder.
The keyword value isn’t as important in terms of SEO as it used to be, however it’s not a complete waste of time to include it within the page. The keyword value should contain around 5-10 terms or phrases (separated by commas) that best describe to content of the page. There is no need to make this placeholder mandatory within the page.
I tend to group all Meta data fields together at the top of the page (within a collapsible div) so that users can edit these items quickly and easily.
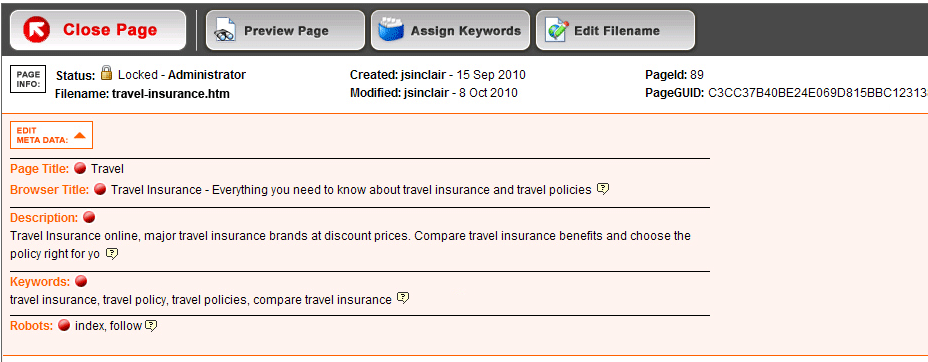
Using the ‘child element’ grouping placeholder feature, clicking on any of these RedDots will automatically pop up a form where the user can edit the title, alternative page title and all meta data properties with one click. Some help text about each of the fields doesn’t go astray either!
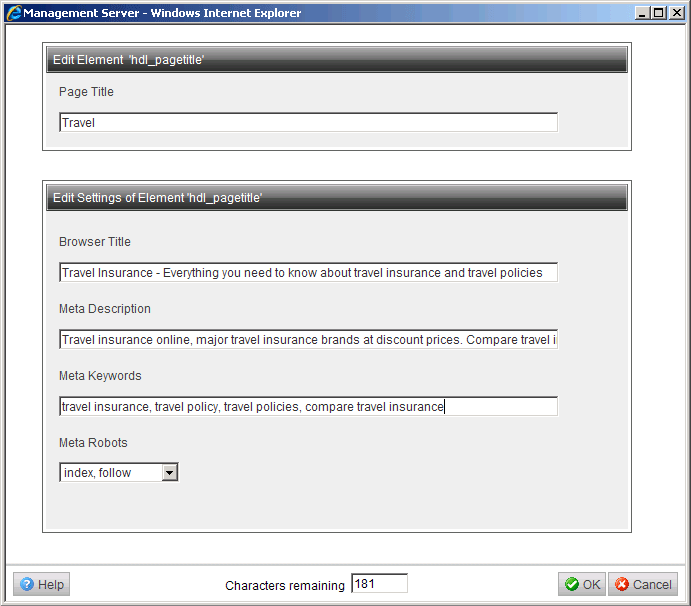
Make your pages easy to use and your authors will love you!
SEO friendly page filenames
The filename for the page is another way in which you are able to target specific page keywords, since search engines reward filenames (as well as domains and directories) that contain keywords and or phrases.
Although RedDot provides the ability to assign a friendly URL to a page, unfortunately this isn’t a mandatory requirement for workflow submission. I’ve found that most users tend to overlook or forget to add a friendly filename, especially when there are pressing deadlines to get content published! By default, RedDot will publish pages as either an integer or GUID filename if this value is left blank.
As a workaround to this, I developed a custom ‘Add Page’ RedDot that I include within my projects that mimics the ‘create and connect’ default method or creating pages – but automatically assign a friendly URL filename based on the page headline when the page is created using RQL.
Whilst working at Areeba, I created two separate plugins (which are available for purchase) that would automatically update the filename for the page whenever the page headline was changed (using JQuery/AJAX/RQL) and the other a separate standalone application that would crawl through a project and assign friendly filenames to pages that did not have one assigned.
Just make sure that you limit filenames to around 100 characters (as RedDot is unable to publish filenames longer than this due to a ‘temp’ folder issue) and use hyphens instead of spaces.
Sitemap file
Sitemaps are a way to inform search engines about pages within your site that they might not otherwise discover. The easiest way to create a XML Sitemap file for your site is to output page links using the Navigation Manager. Since the Navigation Manager already has a tree representation of all your site pages, there’s no need to utilise lists or anchors to build the file.
Check out Google Webmaster Central for more information regarding format of Sitemap files.
Robots.txt
The robots.txt file provides search engine crawlers (or robots) instructions on which parts of the sites to crawl and or index.
Just make sure that the robots.txt file sits within the root folder of your site. You can either incorporate the file within your CMS project as a ‘linked’ media file (from a main menu page or the homepage) or a separate page published by the CMS that is created from a static content class template.
Everything you need to know about robot.txt files can be found at http://www.robotstxt.org.
404 error pages
Incorporate a custom 404 error page within every project that you build to catch any mistyped URL’s or broken links. Whenever a user comes across a broken link, the last thing you want is visitors to leave the site, so as a minimum your 404 error pages should contain the following:
- An apology for the error
- A link to your site map
- A link to your home page
- Links to the other main areas of your site
- A prominent search box (if search is enabled within your site)
By integration some custom server-side code, you can also use your 404 error pages to manage 301 redirects within your site (which I’ll get around to blogging about in the near future!)
Image alt text
Set the alt value to ‘required’ for all image placeholders to ensure authors add relevant textual descriptions for image content (another way to target page keywords!)
Links displayed within html only (No JavaScript)
Always make sure that your navigational links are contained within the HTML source of the page. By all means necessary, avoid outputting navigational links within JavaScript code otherwise search engines won’t be able to crawl your site links.
Provide alternative text content for flash movies
Since search engines are unable to index content within flash, make sure you provide users within the ability to provide ‘no-flash content’ for this purpose. A simple Text placeholder will serve this purpose.
When it comes to SEO, the important thing to note is that there are no hard and fast rules. SEO is will continually keep evolving as long as search algorithms continually keep changing. The most important thing is to ensure that you adopt as many industry best practises as possible as a well optimised site will do much better than a site that doesn’t.
Feel free to share any other SEO hints and tips that you use within your projects!